
OAE Hearing Tests - A Beginner’s Guide
Search for articles by category
Hearing health can be complex, but thanks to new technology, it's now easier to get a clear picture of what's happening inside your ear.
A great example of this is Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) testing. This quick, non-invasive test that tells us how well your inner ear is working. Devices that used to be bulky and costly, have become much more portable and affordable, making them a more accessible tool for audiology professionals and their patients.
In this blog, we’ll give you answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about OAE assessments.
1. What is an OAE assessment?
An OAE hearing test is a quick, non-invasive procedure used to assess the function of the inner ear's outer hair cells. These tiny, delicate cells in the cochlea are crucial for amplifying low-level sounds.
2. How do OAE assessments work?
During an OAE assessment a stimulus is presented, the outer hair cells respond by generating a faint echo that travels back out of the inner ear, through the middle ear, and into the ear canal. A specialized instrument – known as a probe – is placed in the ear canal and detects this echo.
If echoes are present, it indicates that the outer hair cells in the cochlea are functioning as expected.
In contrast, their absence suggests a potential issue in the auditory pathway, which may be due to damage to the outer hair cells or other factors, such as middle ear problems that block the signal.
3. What’s the difference between TEOAEs and DPOAEs?
Two of the most common OAE assessments include TEOAEs and DPOAEs, each with a distinct clinical application.
Transient-Evoked Otoacoustic Emissions (TEOAE): A TEOAE hearing assessment uses a brief series of broadband click sounds to test the outer hair cells of the cochlea. The click stimuli alternate in level and polarity, leading to the non-linear response that quantifies the OAE.
TEOAEs are typically conducted across a range up to 4 kHz and their efficiency makes them particularly useful to assess newborns and infants, or patients with limited response capability due to developmental disabilities or injury.
Distortion Product Otoacoustic Emissions (DPOAE): A DPOAE assessment uses two simultaneous tones of different frequencies (f1 and f2). A healthy cochlea's outer hair cells respond by producing a distortion product tone at the specific test frequency (2f1−f2).
DPOAEs can be measured across a broader and higher frequency range than TEOAEs, , providing a more detailed assessment. DPOAE testing is valuable in clinical audiology for monitoring changes in hearing, such as those caused by ototoxic medications, noise exposure or intracochlear pressure variation.
4. How do I interpret OAE results?
The results of an OAE assessment are a “window” into the inner ear’s health, but their interpretation depends on the type of assessment you conduct. Newer devices on the market can offer both screening and diagnostic functionalities with the same hardware, enabling you to save on equipment costs.
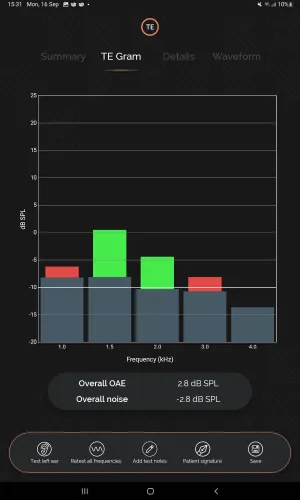 Figure 1: Example of a TE gram*
Figure 1: Example of a TE gram*
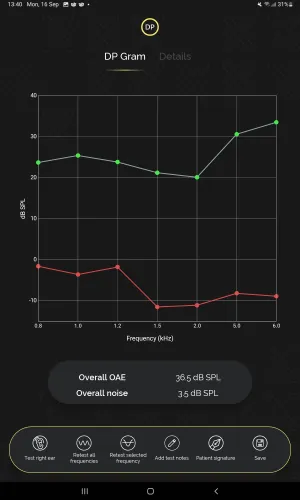 Figure 2: Example of a DP gram*
Figure 2: Example of a DP gram*
Screening vs diagnostic assessments
OAE screenings provide a "PASS" or "REFER" result. A "PASS" suggests that there’s a relatively low chance a patient might have an auditory disorder that requires further assessment.
A "REFER" result means the test criteria weren't met. It doesn't definitively mean hearing loss is present, however, further hearing testing is recommended to establish why. This is a crucial distinction.
The absence of OAEs could be due to a variety of factors – both pathological and non-pathological – including middle ear issues like fluid or earwax, or simply poor probe placement.
For diagnostic assessments, results are presented on a DP gram with three possible outcome categories:
-
DPOAE is absent,
-
DPOAE is present and normal, or
-
DPOAE is present but not normal.
It should be noted that OAE assessments can’t establish the degree of hearing loss, as with pure tone audiometry, which is why OAE assessments are recommended as part of a comprehensive test battery. Given that OAEs are more sensitive to identifying potential hearing issues at inner ear level, this makes them indispensable to support timely intervention and follow-on care.
*Please note:
The hearOAE device settings are customizable based on the tester's preference. Results will differ based on the settings selected and the type of assessment conducted.
OAE technology—More than a research tool
Navigating hearing care has become simpler thanks to advancements in Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) technology. It's no longer just a research tool; it’s now an essential part of modern hearing assessments.
Understanding the benefits of OAEs
By understanding the differences between Transient Evoked (TE) and Distortion Product (DP) assessments, you can gather more information into your patients’ inner ear health. These objective, non-invasive tests save you time and provide the critical information you need to make confident clinical decisions.
In today's fast-paced healthcare environment, having a versatile and reliable OAE device is a necessity. The right technology can help you confidently screen patients, interpret results, and guide your next steps.
Introduce the hearOAE device to your practice
To bring this powerful technology into your practice, consider the hearOAE device, which is part of the comprehensive hearX suite of digital audiology solutions. It's designed to help you confidently screen patients, interpret their results, and guide your clinical decisions with ease.
To learn more about how hearOAE can transform your practice request a demo today:
Email us or call:
US: +1 (415) 825-3064 | RSA: +27 (0) 12 030-0268



